Retinal Detachment: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
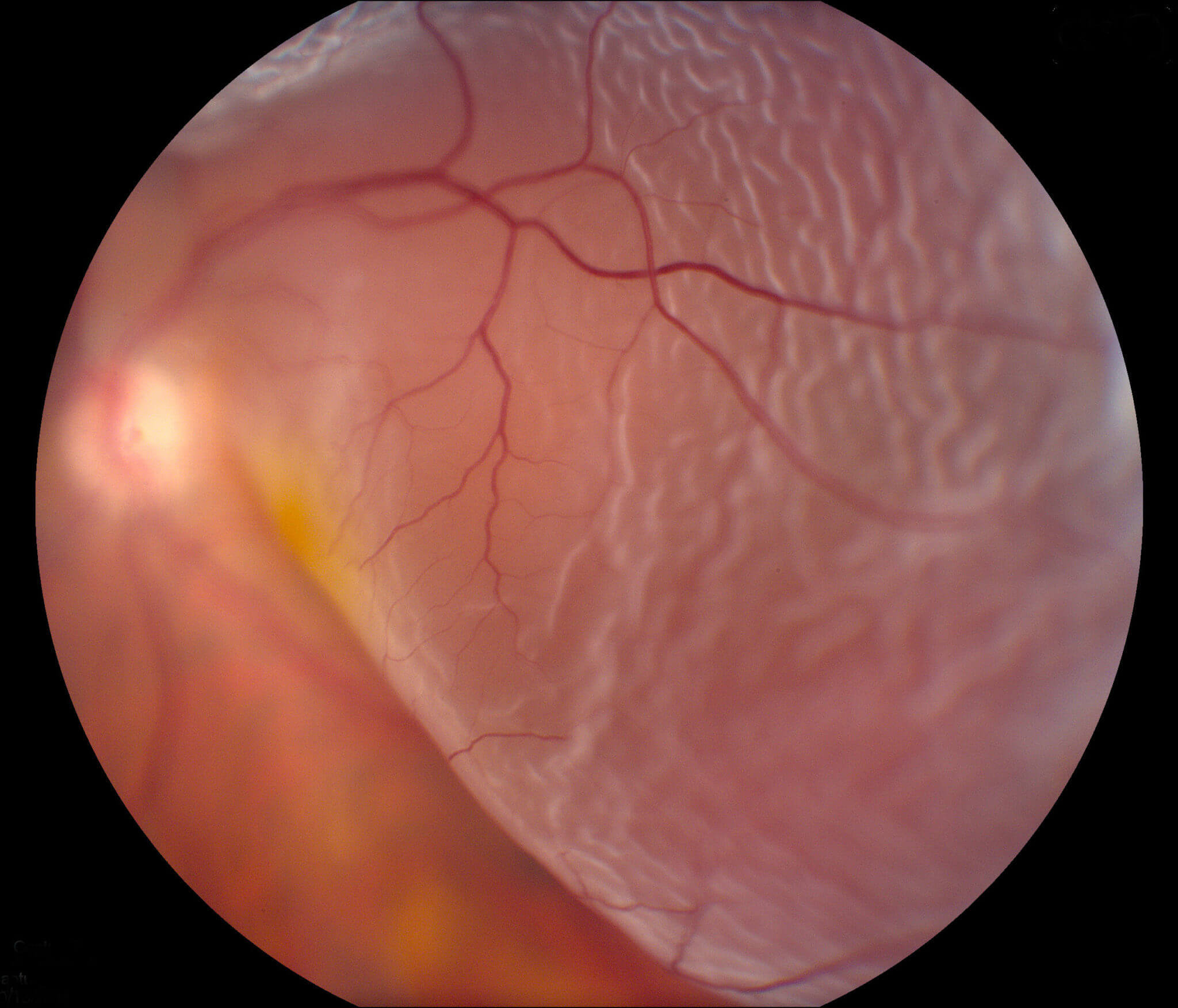
Causes of Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment can be caused by several factors, including:
- Age-related changes to the vitreous, the gel-like substance that fills the eye
- Eye injury or trauma
- Family history of retinal detachment
- Nearsightedness
- Previous eye surgery
Symptoms of Retinal Detachment
The symptoms of retinal detachment can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Flashes of light or floaters in the field of vision
- A shadow or curtain over part of the visual field
- A sudden decrease in vision
Treatments for Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment requires prompt medical treatment to prevent permanent vision loss. Some common treatments include:
- Laser surgery to re-attach the retina
- Cryopexy, which uses extreme cold to seal the retina back into place
- Scleral buckle surgery, which involves placing a silicone band around the eye to support the retina
Prevention of Retinal Detachment
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent retinal detachment, some steps can be taken to lower your risk, including:
- Having regular eye exams to monitor for changes in the eye
- Wearing protective eyewear during high-risk activities, such as sports or construction work
- Managing underlying conditions that increase the risk of retinal detachment, such as diabetes
FAQs
What causes retinal detachment?
Retinal detachment can be caused by several factors, including age-related changes to the vitreous, eye injury or trauma, family history of retinal detachment, nearsightedness, and previous eye surgery.
What are the symptoms of retinal detachment?
The symptoms of retinal detachment can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include flashes of light or floaters in the field of vision, a shadow or curtain over part of the visual field, and a sudden decrease in vision.
How is retinal detachment treated?
Retinal detachment requires prompt medical treatment to prevent permanent vision loss. Some common treatments include laser surgery to re-attach the retina, cryopexy, which uses extreme cold to seal the retina back into place, and scleral buckle surgery, which involves placing a silicone band around the eye to support the retina.
Can retinal detachment be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent retinal detachment, some steps can be taken to lower your risk, such as having regular eye exams, wearing protective eyewear during high-risk activities, and managing underlying conditions that increase the risk of retinal detachment, such as diabetes.
