Abortion Laws by State
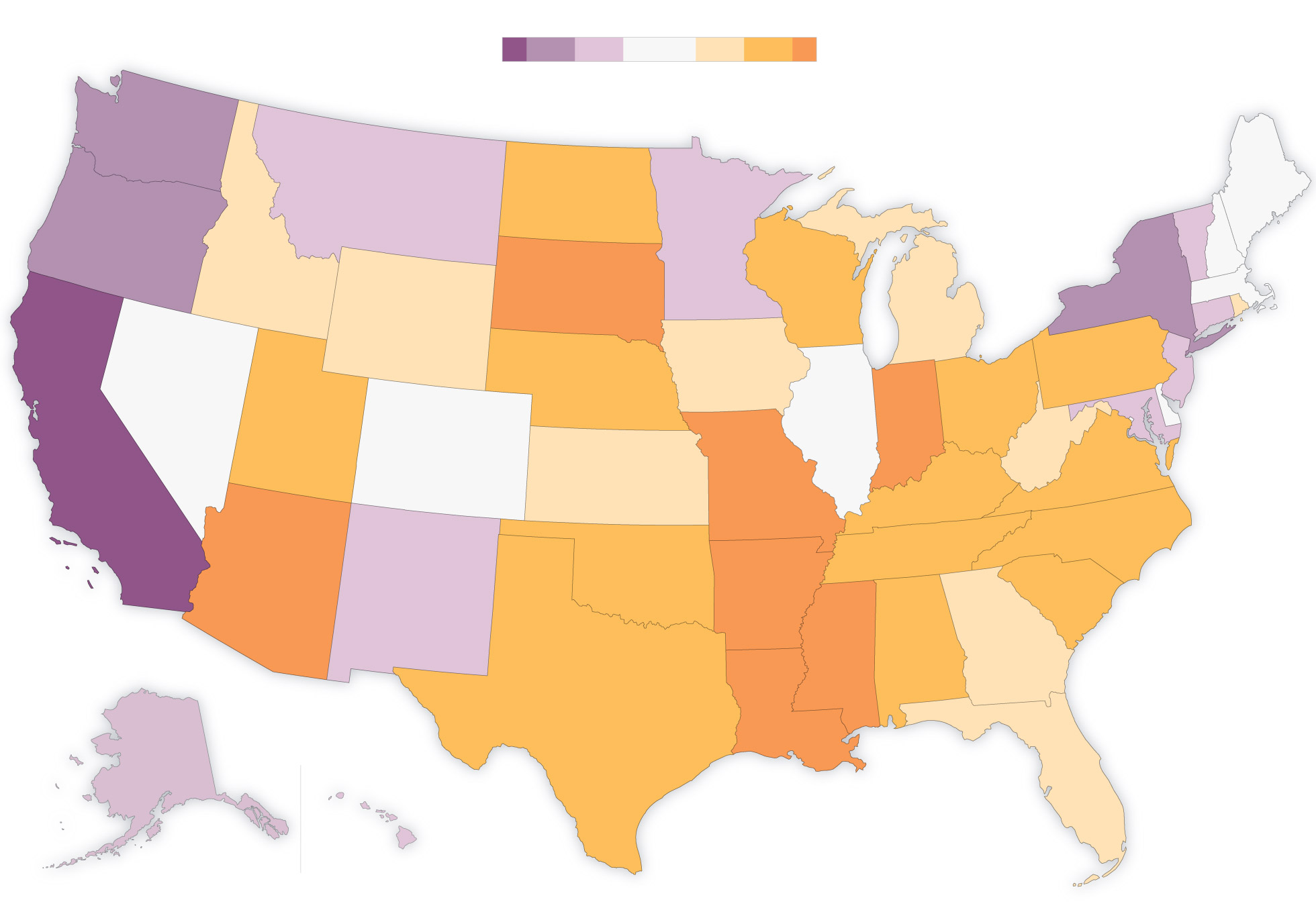
Current Abortion Laws by State
Abortion laws in the United States are constantly changing, and it can be difficult to keep up with the latest regulations. However, as of 2021, the following is a brief overview of the abortion laws by state:
States with Liberal Abortion Laws
California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Illinois, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Montana, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Oregon, Rhode Island, Vermont, Washington, and Washington D.C. all have relatively liberal abortion laws. These states generally do not place many restrictions on abortion access.
States with Moderate Abortion Laws
Alaska, Florida, Idaho, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Michigan, Missouri, Nebraska, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, Utah, Virginia, West Virginia, and Wisconsin have moderate abortion laws. These states have some restrictions on abortion access, but they are not as strict as in conservative states.
States with Strict Abortion Laws
Alabama, Arkansas, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Texas have some of the strictest abortion laws in the country. These states have passed laws that make it difficult or impossible for women to access abortion services. For example, some states require women to undergo an ultrasound before getting an abortion, while others require a waiting period of 24-72 hours before the procedure can be performed.
Why Do Abortion Laws Vary So Much by State?
The answer to this question is complex and multifaceted. One reason is that the United States has a federal system of government, which means that states have a certain degree of autonomy to pass their own laws. Additionally, different states have different political climates and values, which can influence the laws that are passed.
The Pros and Cons of Abortion Laws by State
Pros
- States can pass laws that reflect their own values and priorities.
- States can regulate abortion to ensure that it is safe for women.
- States can restrict abortion access to reduce the number of abortions that are performed.
Cons
- Abortion laws by state can create inequality and restrict access to healthcare for women.
- States can pass laws that are unconstitutional or violate a woman's right to choose.
- Abortion laws by state can be confusing and difficult to navigate, particularly for women who live near state borders.
FAQs
Q: What is the current status of Roe v. Wade?
A: Roe v. Wade is still the law of the land, but it has been weakened by subsequent Supreme Court decisions and state laws that restrict abortion access.
Q: Can states ban abortion outright?
A: No. The Supreme Court has ruled that a woman has a constitutional right to an abortion. However, states can regulate abortion access to some degree.
Q: Do abortion laws by state affect women who live near state borders?
A: Yes. Women who live near state borders may need to travel to another state to access abortion services, depending on the laws in their state.
Q: Are there any federal laws that regulate abortion?
A: Yes. The Hyde Amendment prohibits federal funding for abortion services, and the Partial-Birth Abortion Ban Act prohibits a specific type of abortion procedure.
